SYSTEMS DESIGN
BRIEF
Develop a detailed visual map of the Respite Care System in Australia and identify areas opportunities for innovation that focus on social impact.
DESIGN SOLUTION
For this group project, three system maps were developed. Two maps detail various aspects of the respite care system in Australia and the other shows elderly’s daily activities. Donut Robot was designed to improve elderly mobility, independence and overall health.
TOOLS AND SOFTWARE
Autodesk Fusion 360
Autodesk Sketchbook
Analogue Sketches
Miro
PowerPoint
SurveyMonkey
RESPITE CARE IN AUSTRALIA
BRAINDUMP MAP

BACKGROUND
The purpose of this project was to understand the Respite Care System in Australia through system mapping to identify problems or areas of opportunities for a design intervention. The area of focus of this project was service delivery (highlighted in yellow in the map above).
RESEARCH
Extensive primary and secondary research was conducted for this project.
Primary research - 6 Interviews: 4 respite care recipients/families and 2 staff members with over 20 years of experience.
Secondary research - 24 Government and 8 Private Organisation online sources (including respite care service providers websites) .
PROBLEMS & OPPORTUNITIES
One of the largest problem experienced by elderly in Respite Care services is Mobility. This is due to the direct impact it has on their health, activities seniors perform and on the increased dependency it creates on carers.
DESIGN SOLUTION
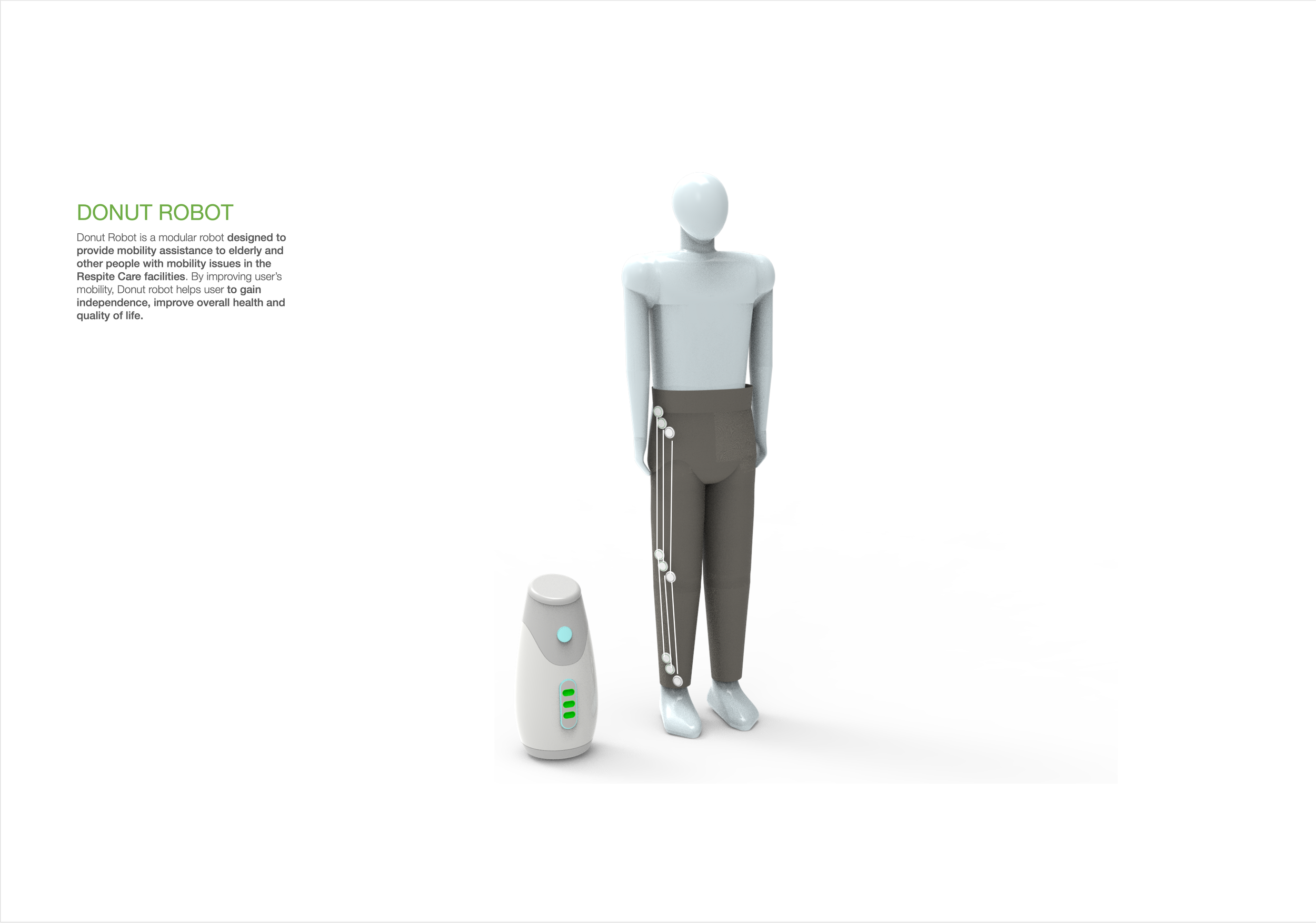
Donut Robot was designed to address seniors mobility issues within Respite Care facilities in Australia. Donut robot is a modular robot designed to provide mobility assistance to elderly and other people with mobility issues to improve their health, quality of life and gain independence.
RESPITE CARE FACILITIES
BRAINDUMP MAP
ORIGINAL SYSTEM
The original system faced 4 complexities; complexity no.1 point of influence - the elderly (the most dependent and vulnerable user) and no. 2 the important transition between mobility and walking. Complexity no. 3 mobility due to the direct impact it has their quality of life, overall health and and direct connection on activities they perform. Complexity no. 4 delayed feedback from medical practitioners on elderly health assessments and treatments.
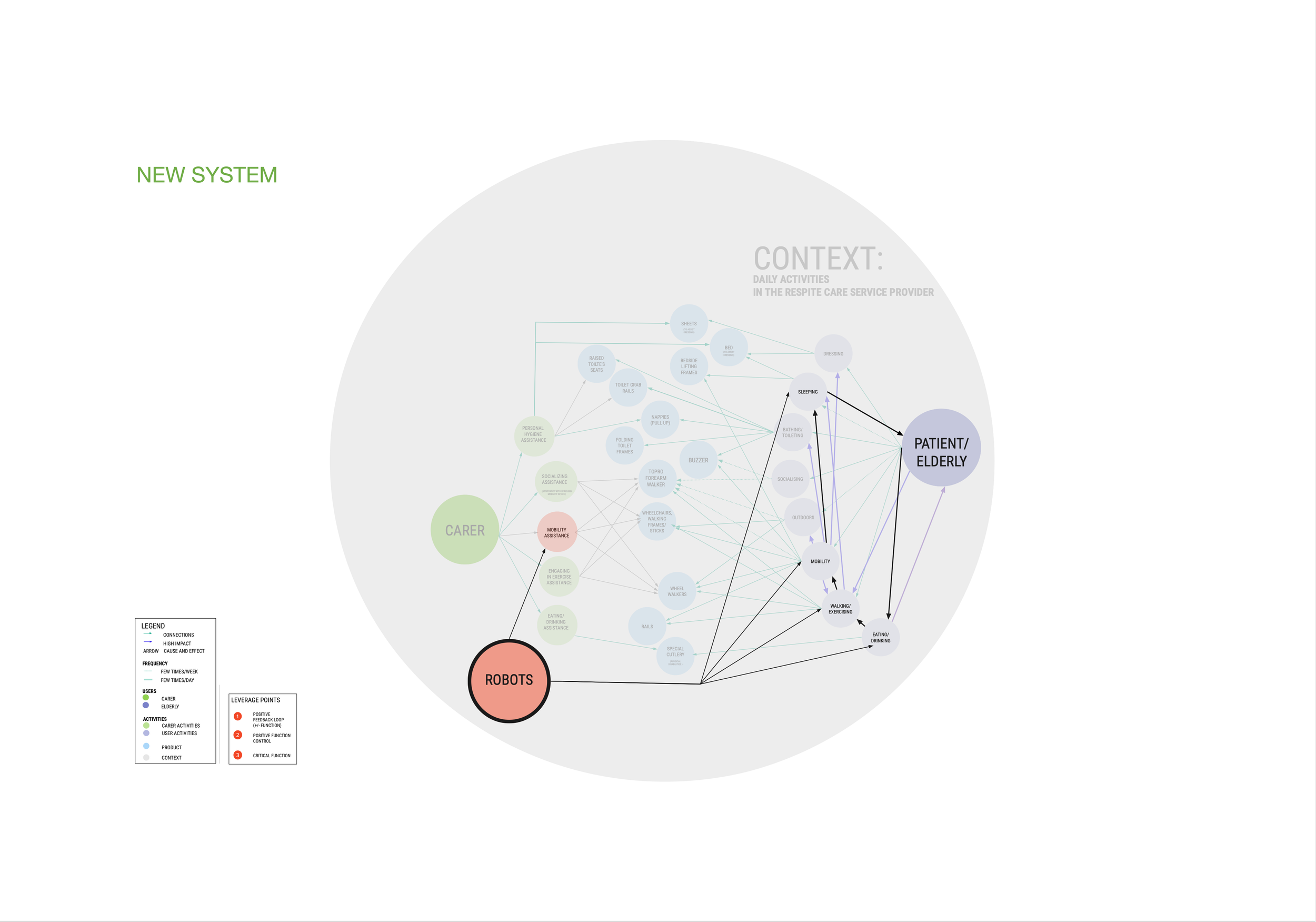
NEW SYSTEM
All complexities are significantly improved in the new system with the implementation of the robot. Complexity no. 1- seniors’ quality of life and overall health improve, and their independence increases by using robots to increase mobility. Complexity no. 2 - walking increases, as user’s mobility increases. Complexity no. 3 – as user’s mobility improves, so it does all activities mobility is connected to. Complexity no. 4 - delayed feedback from medical professionals is reduced through real time health data made available by the robots daily.
SENIORS’ DAILY ACTIVITIES
PACT MAP
ORIGINAL SYSTEM
Three complexities were identified for this system mapping. Complexity no. 1 – the positive feedback loop between the elderly, mobility, sleeping, eating/drinking and walking/exercising. Complexity no. 2 – mobility assistance and wheeled walkers which impact the positive feedback loop and Complexity no. 3 – critical function being the carer due to the great dependency elderly has on carers which directly impacts on elderly’s overall health and quality of life.
NEW SYSTEM
All complexities are significantly improved after introducing robots in the elderly’s day to day life. Complexity no. 1 - the positive feedback loop is improved by increasing mobility with the use of robots which are designed to increased user’s mobility. Complexity no. 2 positive function control (mobility assistance) is also improved. Robots are used by the elderly to assist them with mobility and increase their mobility over time. No. 3 – critical function - the carer. Mobility assistance provided by the carer is now provided by the robot, thus helping elderly gain more control and independence.
DESIGN SOLUTION
DONUT ROBOT
USER EXPERIENCE MAP
This user experience shows how the product affects user’s mobility when going to socialize after waking up from a nap.
Level of mobility directly impacts the user’s ability to perform activities such as walking, socializing and exercising.
The robot helps the user move with much more ease and increase their mobility over time.
The elastic bands that connect the robots expand and contract to help the user move specific body parts with less effort. This facilitates walking, sitting and getting up.
DESIGN PROCESS OVERVIEW
Users’ & context Research
System research
User interviews
Market research
Brainstorming & Ideation
Concept iteration
Concept Development
Concept Refinement
Final system mappings, design & presentation boards